General Overview of All Types of Chargers
Product Overview > General Overview of All Types of Chargers
Charger and its working with its terminology
Electric vehicle (EV) chargers are devices designed to replenish the battery of an electric vehicle with electrical energy. They come in various types and configurations, each offering different charging speeds and capabilities. Here's a description of common EV chargers and how they operate:
Level 1 Chargers:These chargers typically use a standard 120-volt household outlet and are the slowest option for charging an EV. They are convenient for overnight charging at home but may take several hours to fully charge the vehicle's battery, depending on its size and capacity.
Level 2 Chargers: Level 2 chargers operate on a 240-volt circuit, providing faster charging compared to Level 1 chargers. They are commonly found in residential settings, workplaces, and public charging stations. Level 2 chargers can fully charge an EV in a matter of hours, making them suitable for daily charging needs.
DC Fast Chargers (Level 3): DC fast chargers are the quickest option for charging EVs and are primarily used for rapid charging at public charging stations. Unlike Level 1 and Level 2 chargers, which convert alternating current (AC) from the grid to direct current (DC) for charging the vehicle's battery, DC fast chargers supply DC power directly to the vehicle's battery. This allows for significantly faster charging times, with some DC fast chargers capable of providing an ~80% charge in as little as 30 minutes.
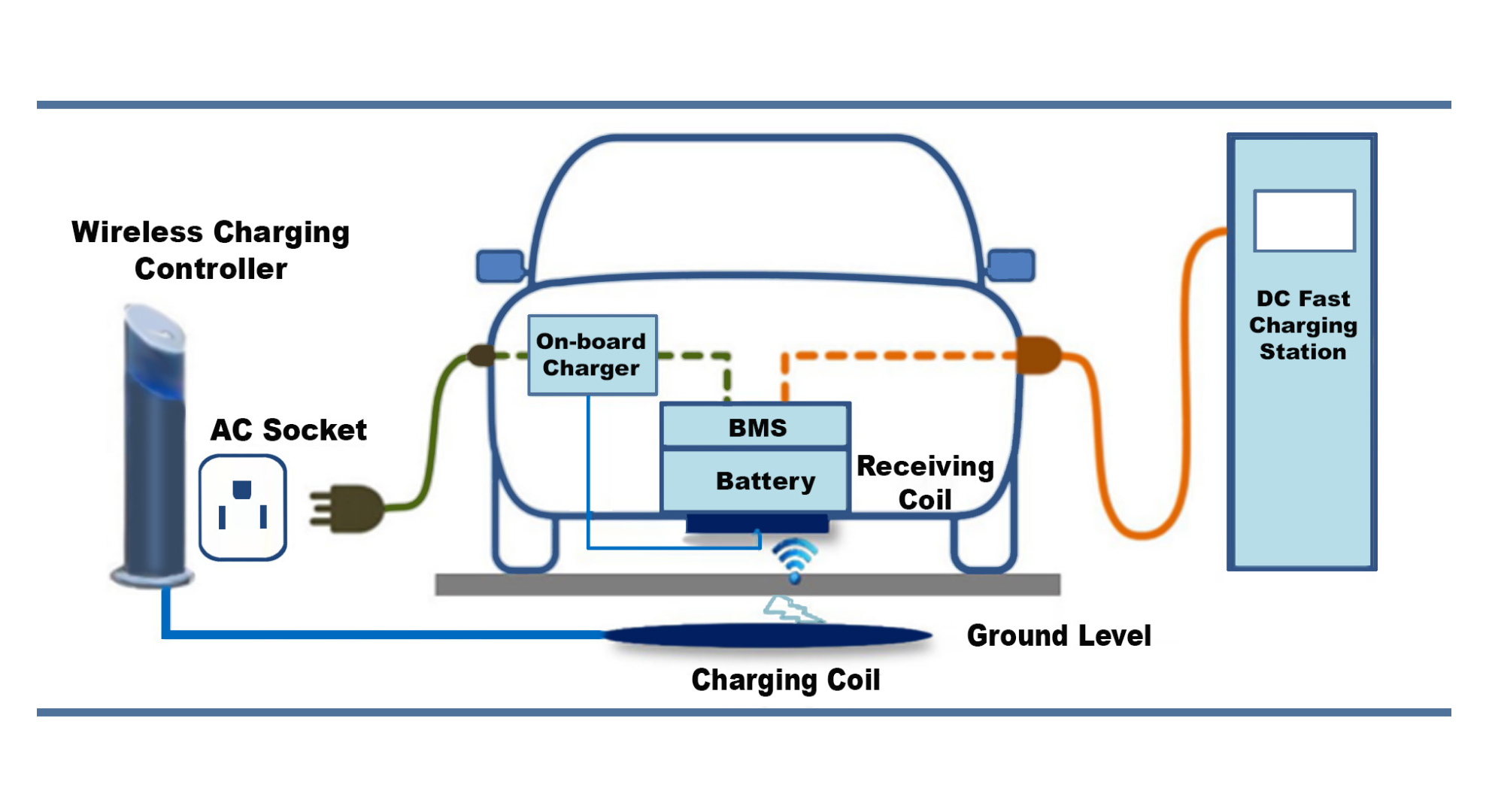
Wireless Chargers: Wireless EV chargers, also known as inductive chargers, utilize electromagnetic fields to transfer energy from a charging pad to a receiver coil installed in the vehicle. The process, known as electromagnetic induction, eliminates the need for physical cables and connectors, offering a convenient and hassle-free charging experience. However, wireless chargers typically have lower charging speeds and are less efficient compared to wired chargers.
The operation of EV chargers involves several steps:
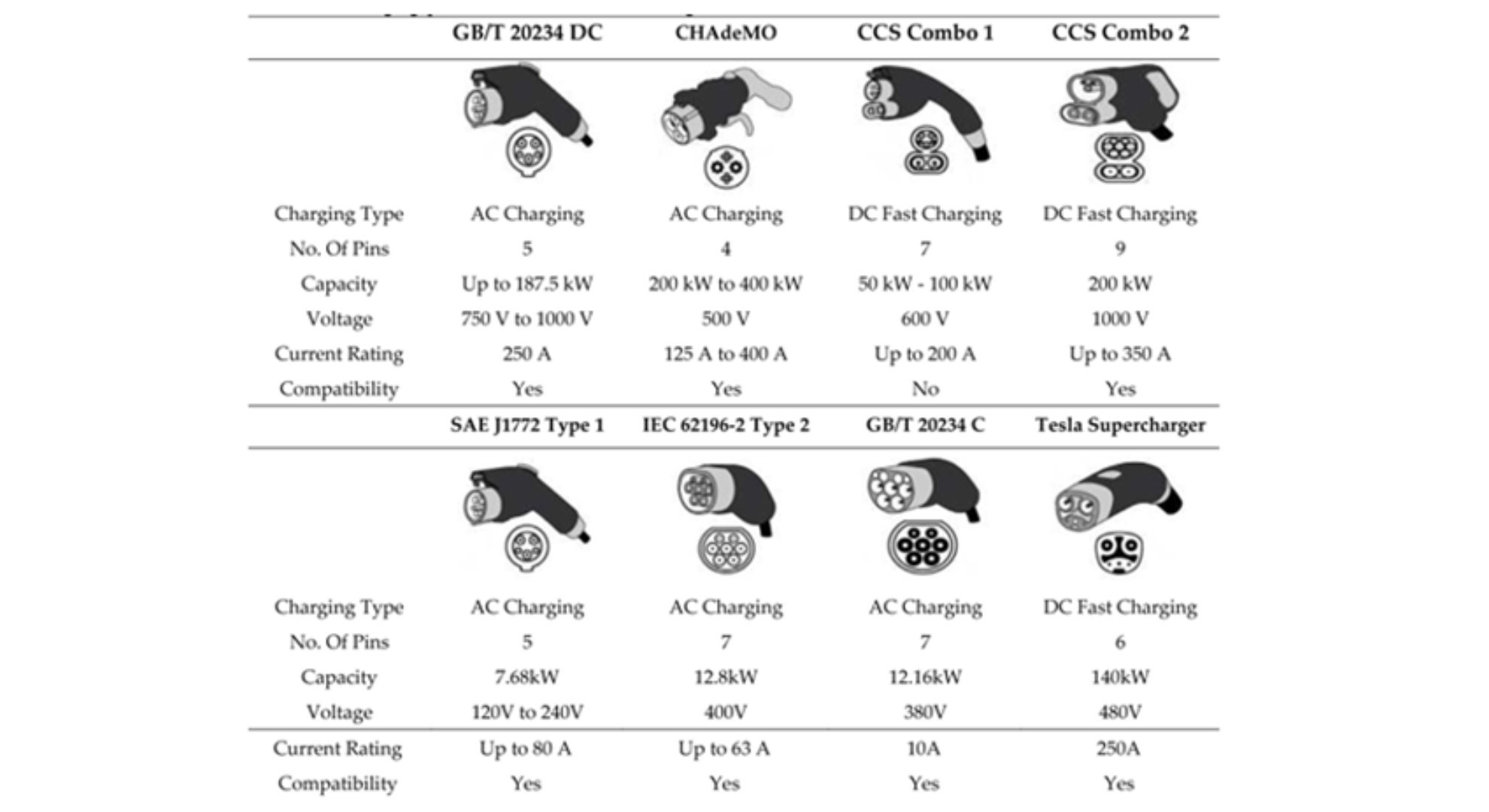
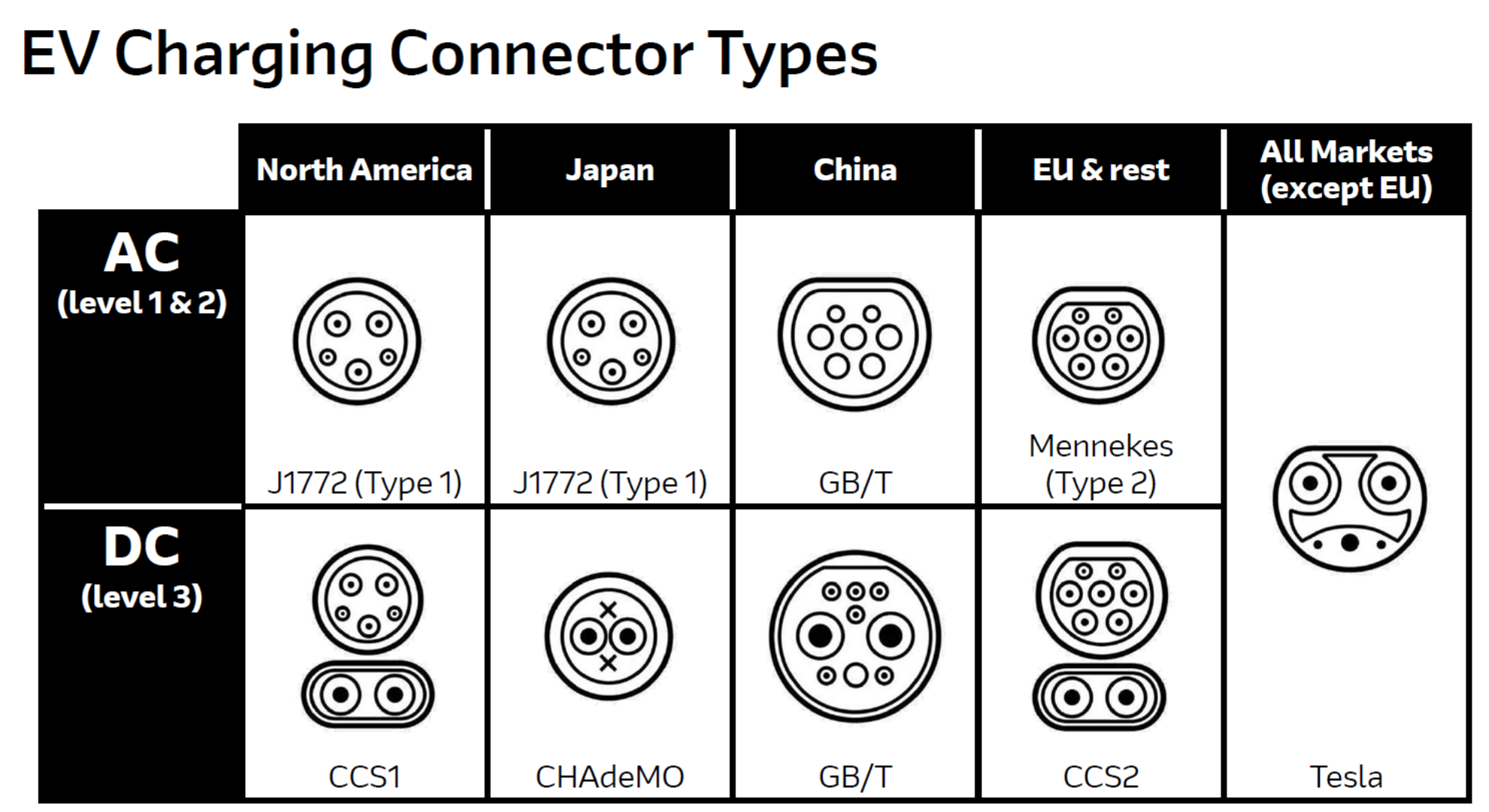
Connection: The EV driver connects the charging cable to both the EV's charging port and the charger unit. Today there are many versions of these charging ports.
Authentication: Some charging stations require authentication before initiating the charging process. This can involve using a mobile app, RFID card, or touchscreen interface to confirm the user's identity and authorize the charging session.
Charging Protocol: Once authenticated, the charger communicates with the vehicle to establish the appropriate charging protocol, including the voltage and current levels to be delivered to the battery.
Charging: The charger supplies electrical power to the vehicle's battery, which converts it to chemical energy for storage. The charging process continues until the battery reaches its maximum capacity or until the user interrupts the session.
Monitoring: Throughout the charging process, the charger monitors various parameters such as voltage, current, and temperature to ensure safe and efficient charging. Some chargers also provide real-time charging status updates to the user via mobile apps or display screens.
Completion: Once the charging session is complete, the charger terminates the power supply, and the user can disconnect the charging cable from the vehicle.
Overall, EV chargers play a critical role in enabling the widespread adoption of electric vehicles by providing convenient and efficient charging solutions for drivers.